
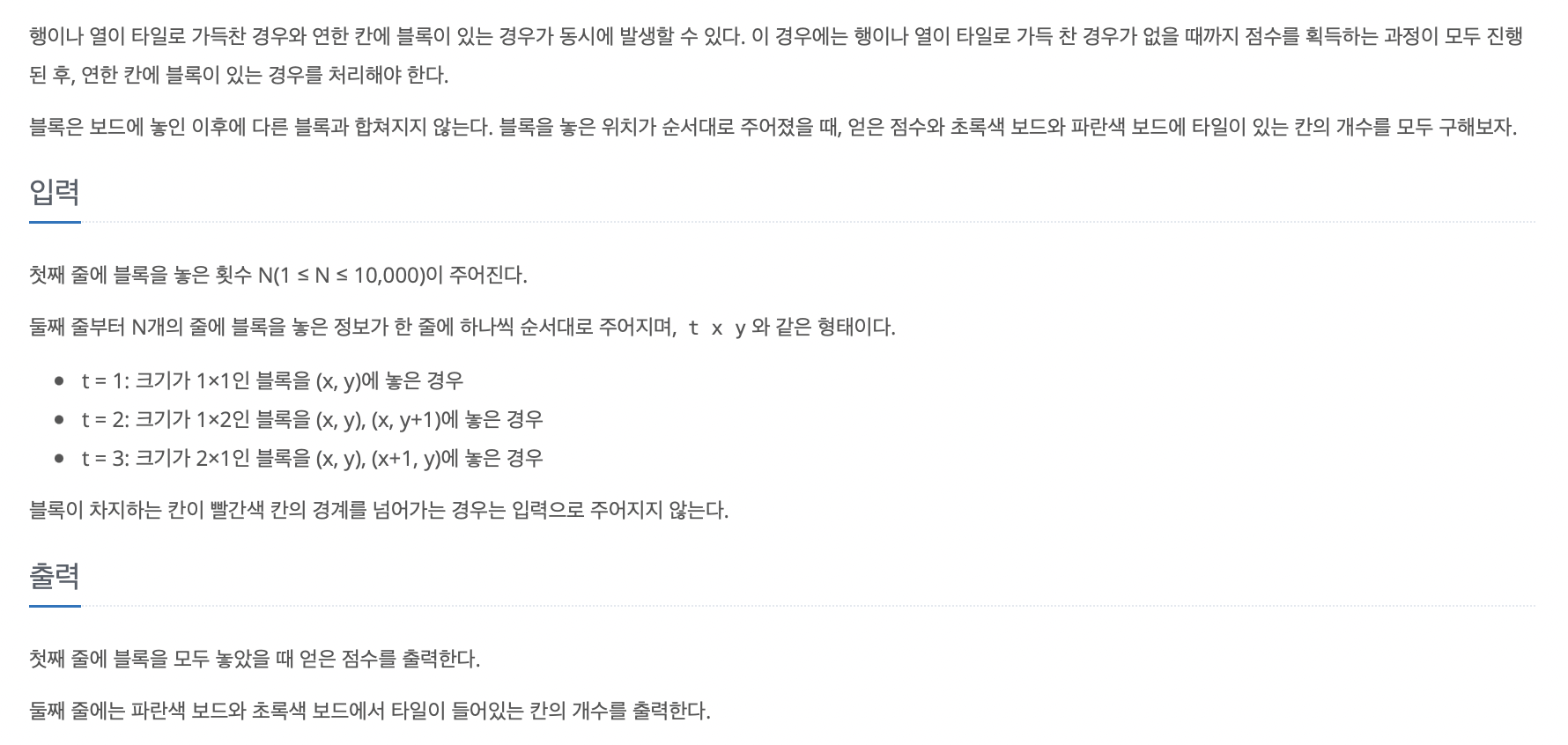
이 문제는 그림으로 하나하나 어떻게 동작하는지 잘 설명해주어서 이해하기가 조금은 수월했다.
'조금'이라는 표현을 한 이유는 문제에서 일어날 수 있는 다양한 예시를 보여줬다기 보다는 어떤 한 예시를 통해 각각의 단계별로 보여줬기 때문에 테스트 케이스를 다 통과한다 할지라도 틀릴 수 있고, 구현이 잘못된 부분이 있을지라도 테스트 케이스를 통과할 수 있었다.
(예를 들면, blue칸에서 이동하는 것을 잘못 짰는데 blue에서 그런 이동이 없는 경우 테스트 케이스를 돌리더라도 발견할 수 없다.)
물론 이러한 예외 사항들은 본인이 직접 찾아가며 하는 것이 당연하지만 그냥 투정이라고 생각해주면 좋겠다.
코드
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
|
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int N;
typedef struct block
{
int t,x,y;
}block;
block b[10001];
int red[4][4];
int green[6][4];
int blue[4][6];
void move(int mode)
{
if (mode == 0)
{
for(int i=4; i>=0; i--)
{
green[i + 1][0] = green[i][0];
green[i + 1][1] = green[i][1];
green[i + 1][2] = green[i][2];
green[i + 1][3] = green[i][3];
}
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
green[0][i] = 0;
}
else if (mode == 1)
{
for(int i=4; i>=0; i--)
{
blue[0][i + 1] = blue[0][i];
blue[1][i + 1] = blue[1][i];
blue[2][i + 1] = blue[2][i];
blue[3][i + 1] = blue[3][i];
}
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
blue[i][0] = 0;
}
}
void special_check(int mode)
{
if (mode == 0)
{
int row_cnt = 0;
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
if (green[0][j] != 0)
{
row_cnt++;
break;
}
}
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
if (green[1][j] != 0)
{
row_cnt++;
break;
}
}
for(int j=0; j<row_cnt; j++)
move(0);
}
else if (mode == 1)
{
int col_cnt = 0;
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
if (blue[j][0] != 0)
{
col_cnt++;
break;
}
}
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
if (blue[j][1] != 0)
{
col_cnt++;
break;
}
}
for(int j=0; j<col_cnt; j++)
move(1);
}
}
int fill_check(int mode)
{
int change = 0;
if (mode == 0)
{
for(int i=5; i>=2; i--)
{
int cnt = 0;
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
if (green[i][j] != 0)
cnt++;
}
if (cnt == 4)
{
for(int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
green[j + 1][0] = green[j][0];
green[j + 1][1] = green[j][1];
green[j + 1][2] = green[j][2];
green[j + 1][3] = green[j][3];
}
i++;
change++;
}
}
}
else if (mode == 1)
{
for(int i=5; i>=2; i--)
{
int cnt = 0;
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
if (blue[j][i] != 0)
cnt++;
}
if (cnt == 4)
{
for(int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
blue[0][j + 1] = blue[0][j];
blue[1][j + 1] = blue[1][j];
blue[2][j + 1] = blue[2][j];
blue[3][j + 1] = blue[3][j];
}
i++;
change++;
}
}
}
return change;
}
int tile_count(int mode)
{
int cnt = 0;
if (mode == 0) // 초록
{
for(int i=2; i<6; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
if (green[i][j] != 0)
cnt++;
}
}
}
else if (mode == 1) // 파란색
{
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
for(int j=2; j<6; j++)
{
if (blue[i][j] != 0)
cnt++;
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
cin.tie(NULL);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> N;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
cin >> b[i].t >> b[i].x >> b[i].y;
int score = 0;
int total = 0;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
int type = b[i].t;
int x = b[i].x; int y = b[i].y;
if (type == 1)
{
int nx = x; int ny = 0;
while (ny < 5)
{
if (blue[nx][ny + 1] == 0)
ny++;
else break;
}
blue[nx][ny] = type;
nx = 0; ny = y;
while (nx < 5)
{
if (green[nx + 1][ny] == 0)
nx++;
else break;
}
green[nx][ny] = type;
}
else if (type == 2)
{
int nx = x, ny = 1;
while (ny < 5)
{
if (blue[nx][ny + 1] == 0)
ny++;
else
break;
}
blue[nx][ny - 1] = type; blue[nx][ny] = type;
nx = 0; ny = y;
while (nx < 5)
{
if (green[nx + 1][ny] == 0 && green[nx + 1][ny + 1] == 0)
nx++;
else break;
}
green[nx][ny] = type; green[nx][ny + 1] = type;
}
else if (type == 3)
{
int nx = x; int ny = 0;
while (ny < 5)
{
if (blue[nx][ny + 1] == 0 && blue[nx + 1][ny + 1] == 0)
ny++;
else break;
}
blue[nx][ny] = type; blue[nx + 1][ny] = type;
nx = 1; ny = y;
while (nx < 5)
{
if (green[nx + 1][ny] == 0)
nx++;
else break;
}
green[nx - 1][ny] = type; green[nx][ny] = type;
}
int rows = 0, cols = 0;
rows = fill_check(0); //green 점수내기
score += rows;
cols = fill_check(1); //blue 점수내기
score += cols;
special_check(0);
special_check(1);
}
total = tile_count(0) + tile_count(1);
cout << score << "\n" << total << "\n";
return (0);
}
|
cs |
main함수에 모든 것을 구현하기에는 너무 코드가 길어질 것 같아 최~대한 함수로 많이 빼자! 라는 생각에 구현해봤는데도 250줄이 넘었다.
지금 생각해보면 Move라는 함수를 green, blue 보드 전체를 이동하는 것이 아닌, 어떤 index를 받아 그만큼만 이동하도록 구현하였다면 아마 코드가 조금은 더 짧아졌지 않았을까 라는 생각을 하지만 일단은 문제가 요구하는대로 코딩을 쭉 해보았다.
우선 각 블록 타입에 따라 내려갈 수 있는 위치를 계산하여 블록의 위치를 정해준 뒤, 각 보드에서 꽉찬부분이 있는지 확인(fill_check)하고 있다면 그 행을 지우면서 점수를 올려주는 방식으로 구현하였다.
또, special_check란, 각 보드에 특별한 칸에 블록이 있는지 확인하여 블록이 들어있는 특별한 행(열)의 개수 만큼 보드를 움직여주는 기능을 하는 함수이다.
N개의 블록에 대해서 모두 처리를 한 뒤, 문제에서 요구하는 점수과 각 보드에 존재하는 블록의 개수를 세어 출력하라고 하였으므로 위와 같이 구현하였다.
'Study > BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| BOJ - 사다리 조작(15684) (0) | 2021.04.22 |
|---|---|
| BOJ - 구슬 탈출 2(13460) (0) | 2021.04.21 |
| BOJ - 어른 상어(19237) (0) | 2021.04.21 |
| BOJ - 행성 터널(2887) (0) | 2021.04.15 |
| BOJ - 다리 만들기 2(17472) (0) | 2021.04.15 |



