

삼성 SWEA A형 기출문제고, MST에 관련한 문제여서 풀어보았다.
코드
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
|
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int N, M;
int map[11][11];
bool visit[11][11];
bool visit2[11][11];
int costs[11][11];
vector<pair<int, int> > v[7];
queue<pair<int, int> > q;
typedef struct graph{
int v1, v2, cost;
}graph;
vector<graph> g;
int dx[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
void init()
{
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
for(int j=0; j<M; j++)
{
visit[i][j] = false;
visit2[i][j] = false;
costs[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
int getRoot(vector<int> &parent, int idx)
{
if (parent[idx] == idx) return idx;
else return parent[idx] = getRoot(parent, parent[idx]);
}
void merge(vector<int> &parent, int a, int b)
{
a = getRoot(parent, a); b = getRoot(parent, b);
if (a == b) return;
else if (a < b) parent[b] = a;
else parent[a] = b;
}
bool comp(graph a, graph b)
{
return a.cost < b.cost;
}
int main()
{
cin.tie(NULL);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> N >> M;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
for(int j=0; j<M; j++)
cin >> map[i][j];
init();
int idx = 1;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<M; j++)
{
if (!visit[i][j] && map[i][j] == 1)
{
q.push(make_pair(i, j));
map[i][j] = idx;
visit[i][j] = true;
v[idx].push_back(make_pair(i, j));
while (!q.empty())
{
pair<int, int> coor = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int k=0; k<4; k++)
{
int nx = coor.first + dx[k];
int ny = coor.second + dy[k];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= N || ny >= M)
continue;
if (!visit[nx][ny] && map[nx][ny] == 1)
{
q.push(make_pair(nx, ny));
visit[nx][ny] = true;
map[nx][ny] = idx;
v[idx].push_back(make_pair(nx, ny));
}
}
}
idx++;
}
}
}
//우랑 하만 체크
for(int i = 1; i < idx; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<v[i].size(); j++)
{
int x = v[i][j].first; int y = v[i][j].second; int cnt = 0;
int tmp_x = x; int tmp_y = y;
while (++tmp_x < N)
{
if (map[tmp_x][y] == map[x][y])
break;
if (map[tmp_x][y] == 0)
{
cnt++;
continue;
}
else if (map[tmp_x][y] != map[x][y])
{
if (cnt >= 2)
{
int v1 = map[x][y];
int v2 = map[tmp_x][y];
if (costs[v1][v2] == 0 && costs[v2][v1] == 0)
{
costs[v2][v1] = cnt;
costs[v1][v2] = cnt;
}
else
{
costs[v1][v2] = min(costs[v1][v2], cnt);
costs[v2][v1] = min(costs[v2][v1], cnt);
}
}
break;
}
}
cnt = 0;
while (++tmp_y < M)
{
if (map[x][tmp_y] == map[x][y])
break;
if (map[x][tmp_y] == 0)
{
cnt++;
continue;
}
else if (map[x][tmp_y] != map[x][y])
{
if (cnt >= 2)
{
int v1 = map[x][tmp_y];
int v2 = map[x][y];
if (costs[v1][v2] == 0 && costs[v2][v1] == 0)
{
costs[v2][v1] = cnt;
costs[v1][v2] = cnt;
}
else
{
costs[v1][v2] = min(costs[v1][v2], cnt);
costs[v2][v1] = min(costs[v2][v1], cnt);
}
}
break;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=1; i<idx-1; i++)
{
for(int j=i+1; j<idx; j++)
{
if (costs[i][j] != 0)
{
graph t;
t.v1 = i;
t.v2 = j;
t.cost = costs[i][j];
g.push_back(t);
}
}
}
sort(g.begin(), g.end(), comp);
int sum = 0;
vector<int> parent(idx);
for(int i=1; i<idx; i++)
parent[i] = i;
int mst_cnt = 0;
for(int i=0; i<g.size(); i++)
{
int v1 = g[i].v1; int v2 = g[i].v2;
if (getRoot(parent, v1) != getRoot(parent, v2))
{
merge(parent, v1, v2);
sum += g[i].cost;
mst_cnt++;
}
}
if (sum == 0 || mst_cnt != idx - 2)
sum = -1;
printf("%d\n", sum);
return (0);
}
|
cs |
풀이 과정을 이러하다.
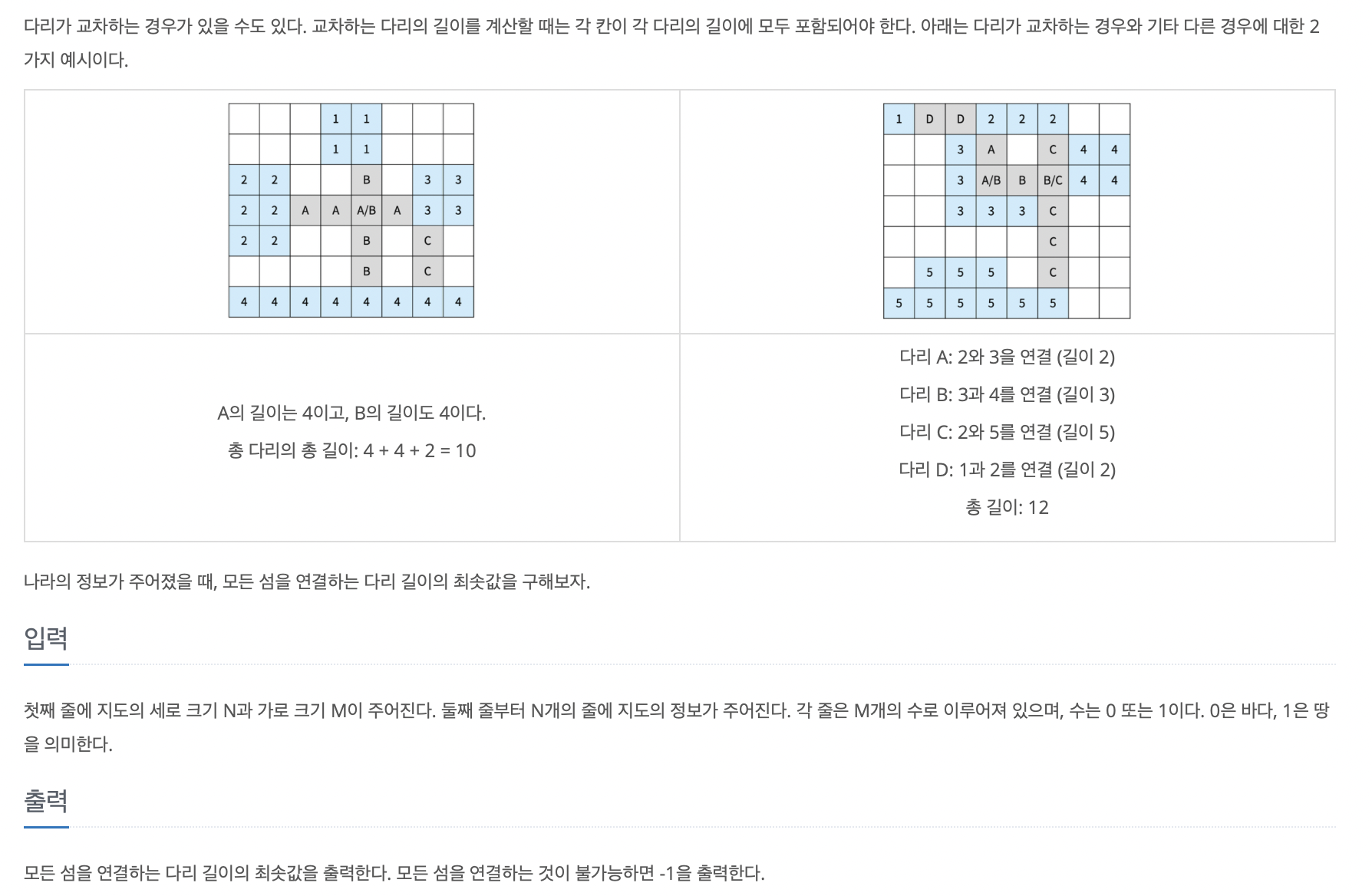
1. 우선 BFS(혹은 DFS)를 이용하여 섬이 몇 개인지, 그리고 각각의 섬을 구분하여야 한다. (map에다가 섬 번호를 넣는 방식으로 구분)
2. 상하좌우를 다 볼 필요 없이, 만약 정점 1, 2가 이어진다고 하면 2, 1은 당연히 이어지는 것이므로 하, 우에 대해서만 확인하여 각 섬이 연결될 수 있는지 확인하였다.
3. 연결될 수 있는 가능성에는 총 2가지가 있다.
3.1. 섬과 섬 사이에 0이 2개 이상 있어야 한다. (다리 길이가 2 이상이므로)
3.2. 같은 섬을 만나면 바로 빠져 나와야 한다. (다리가 꺾이지 않는 직선이기 때문에)
4. 섬과 섬 사이의 다리 길이가 두 섬에 대해서 여러 개 일경우 가장 짧은 다리를 선택한다.
5. 위 정보를 그래프 형식으로 저장하고(V1, V2, cost) Kruskal Algorithm을 수행한다.
6. 주의할 점은 이 문제에서는 모든 그래프가 반드시 연결되는 예시만 input에 들어오는 것이 아니기 때문에 연결되지 않는 경우의 수도 고려해야 한다. (고려하는 방법은 MST이므로 항상 V - 1개의 edge가 선택되기 때문에 mst_cnt를 이용하여 계산하였다.)
'Study > BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| BOJ - 어른 상어(19237) (0) | 2021.04.21 |
|---|---|
| BOJ - 행성 터널(2887) (0) | 2021.04.15 |
| BOJ - 네트워크 연결(1922) (0) | 2021.04.15 |
| BOJ - 거짓말(1043) (0) | 2021.04.14 |
| BOJ - 최소 스패닝 트리(1197) (0) | 2021.04.14 |



